Reactive vs. Proactive Maintenance: What’s the Difference?
The success of your maintenance strategy is at the core of asset management. Companies that don’t make a conscious effort to create a proactive maintenance strategy are just watching revenue go down the drain. Distinguishing your maintenance strategy–taking a reactive vs. a proactive approach–can determine your organization’s fate from an operational efficiency and bottom-line perspective.
In the world of machinery, infrastructure, and technology, breakdowns are not just inevitable but potentially disruptive and costly, and there is a critical difference between reactive and proactive maintenance approaches, and each approach has different impacts on asset performance. Adopting an effective maintenance strategy gives an organization the ability to avert downtime, mitigate expensive repairs, and stave off the specter of emergency breakdowns. In a landscape where unpredictability is a constant, crafting an effective maintenance strategy is a pivotal factor in sustaining success and operational continuity.
What is reactive maintenance?
Reactive maintenance is a mode of asset management that takes action only after a breakdown or malfunction has already occurred. Unlike proactive approaches that prioritize prevention, reactive maintenance centers around addressing issues as they arise, often in a hurried, unplanned manner. Reactive maintenance is characterized by a "fix-on-failure" principle and lacks the foresight to anticipate problems. This makes the business reliant on immediate action following a breakdown. This strategy tends to result in higher downtimes, increased repair costs, and a heightened risk of unforeseen operational disruptions, making it a less cost-effective and efficient choice for organizations seeking to maintain optimal asset performance.
What is proactive maintenance?
Proactive maintenance is a preemptive approach to asset management aimed at preventing critical equipment failures before they happen. By systematically conducting routine inspections, predictive analytics, and timely servicing, proactive maintenance identifies potential issues in advance, allowing organizations to intervene before problems escalate into breakdowns. This method not only curtails downtime and reduces repair expenses but also enhances overall operational efficiency, making it a preferred strategy for enterprises looking to uphold continuous and cost-effective functionality.
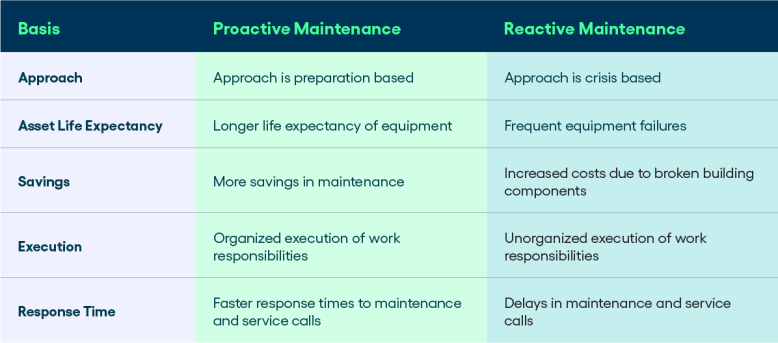
Key differences between reactive and proactive maintenance
Choosing between reactive and proactive maintenance strategies can spell the difference between chaos and control. These approaches stand on opposite ends of the spectrum when it comes to timing and impact. Corrective maintenance’s "fix-it-when-it-breaks" ethos, responds to breakdowns as they occur, often leading to unplanned downtime, soaring repair costs, and operational disruptions.
On the other hand, proactive maintenance adopts a preventive stance. Through regular inspections, data-driven analysis, and timely interventions, preventive maintenance champions the art of avoiding breakdowns altogether, reaping the rewards: reduced downtime, minimized expenses, and sustained operational excellence.
Timing
Reactive maintenance
Reactive maintenance happens after equipment breaks down, which means it's done as a response to a problem that's already occurred. The main disadvantages of reactive maintenance are unexpected downtime and higher costs for repairs.
Proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance is all about planning ahead. It works on a set schedule and involves regular check-ups and preventive actions to stop equipment from breaking down before it even happens. By doing this, it helps avoid unexpected problems and keeps things running smoothly.
Cost
Reactive maintenance
While reactive maintenance might seem cheaper at first, it often ends up being more expensive in the long term. This is because it can lead to emergency repairs, costs from downtime when things aren't working, and even damage to the equipment that could have been prevented with regular upkeep.
Proactive maintenance
Even though proactive maintenance requires an initial investment, it has the potential to save a lot of money in the long run. By stopping big breakdowns before they happen, businesses can avoid expensive emergency repairs and prevent costly periods of downtime.
Asset performance
Reactive maintenance
Reactive maintenance often diminishes performance due to delayed repairs and unresolved issues. This neglect of immediate attention can lead to exacerbated problems resulting in reduced operational efficiency and potentially increased risk of breakdown.
Proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance ensures equipment operates at its optimal level, guaranteeing efficiency and maintaining consistent output through timely inspections, preventive actions, and addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Safety
Reactive maintenance
Unexpected equipment failures can pose serious safety risks, potentially leading to accidents or injuries for workers and anyone in the vicinity.
Proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance identifies and addresses potential hazards before they escalate into significant risks, creating a safer working environment for both employees and those around the equipment.
Strategy & resources
Reactive maintenance
Reactive maintenance involves minimal planning, and resources are allocated on an ad-hoc basis as issues arise. This is a less organized and often rushed approach to addressing equipment problems.
Proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance demands thorough planning, deliberate resource allocation, and establishing a well-structured plan for preventative maintenance, ensuring a systematic and strategic approach to keeping equipment in optimal working condition.
How to transition from a reactive to proactive maintenance strategy: 5 simple steps
Embracing a proactive maintenance strategy can revolutionize the landscape of asset management, ushering in a realm of enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings. A proactive maintenance approach requires meticulous planning and consistent preventive measures. Shifting from a reactive to proactive maintenance strategy involves more than just a change in tactics; it requires a deliberate shift in mindset and a systematic implementation of inspections, predictive analysis, and preventive actions.
1. Conduct a maintenance audit
Creating an effective proactive maintenance strategy starts with a thorough evaluation of current maintenance practices and performance. This involves identifying areas where reactive maintenance prevails and learning the consequences of unplanned downtime and emergency fixes on the larger operational landscape, and its impact on budget allocation.
Defining maintenance key performance indicators (KPIs) is paramount at this step. Organizations should spell out their proactive maintenance goals, whether it's minimizing downtime, prolonging asset lifespans, or optimizing maintenance expenditures. By aligning the strategy with clear objectives, organizations can tailor their approach to yield tangible and strategic benefits, paving the way for sustained success.
2. Prioritize critical assets
By pinpointing the most critical assets within the organization, your organization can prioritize proactive maintenance practices on the assets that wield the most substantial influence on day-to-day operations. By focusing efforts on these pivotal assets, you know the proactive strategy effectively maximizes operational efficiency and minimizes potential disruptions, laying a solid foundation for the broader maintenance plan.
3. Leverage the right technology
Investing in technology like a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), such as Asset Essentials, can streamline your predictive maintenance strategy. Your organization can take advantage of features designed to simplify the proactive maintenance process:
- Asset Tracking: Easily catalog and monitor all your assets in one centralized system
- Work Order Management: Create, assign, and track maintenance tasks efficiently
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilize data analytics to forecast potential issues and plan preventive actions
- Maintenance Scheduling: Set up automated maintenance schedules to ensure timely upkeep
- Mobile Accessibility: Access the CMMS from mobile devices, enabling real-time updates and communication
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate insightful reports on asset performance, maintenance trends, and costs
4. Train and engage the maintenance team
Undoubtedly, the success of a proactive maintenance strategy hinges on a well-informed and empowered maintenance team. A comprehensive training and education program will ensure your staff with the new procedures and processes. A culture of collaboration and continuous improvement ensures a smoother implementation and fortifies the team's ability to effectively carry out their roles, contributing to the organization's sustained efficiency and success.
5. Review and adjust as needed
As your business shifts from reactive to proactive maintenance, regularly evaluating your strategy’s performance against the initial KPIs you've set gives you insights into your successes and your opportunities for improvement. Gathering insights into the strategy's effectiveness and areas allow you to make adjustments where necessary and optimize your strategy.
The journey from a reactive to a proactive approach is a gradual process. It demands unwavering commitment and continual tweaks and adjustments. By conscientiously implementing the steps outlined above, businesses can progress toward a more streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective strategy.
Partner with Brightly to build an effective proactive maintenance strategy
A strong CMMS is vital to enacting a proactive maintenance plan. Brightly can equip your organization with the tools you need to implement a proactive maintenance plan and break free from the dangers of reactive maintenance. Contact a Brightly expert to see which solution will help you establish an effective proactive maintenance strategy for your organization.



